
How Refuse Derived Fuel is Shaping Waste Management in India
Do you know how much municipal solid waste India generates from households, institutions, and businesses each year?
According to the Central Pollution Control Board report, India produces over 160,000 metric tonnes of municipal solid waste (MSW) daily, making waste management one of the nation’s most critical environmental challenges. This waste ranging from food scraps and plastics to textiles and paper is rapidly filling up landfills and polluting ecosystems. Globally, countries like the U.S. generated 254 million tons of MSW in 2013 alone, with only 34.3% recycled or composted. As urbanization grows and consumption increases, traditional waste disposal systems are no longer sustainable.
That’s where Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) comes into play, a smart, eco-friendly solution that transforms non-recyclable waste into usable fuel. In the context of municipal solid waste management in India, RDF technology is helping industries reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimize landfill pressure, and move toward a circular economy.
What is Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)?
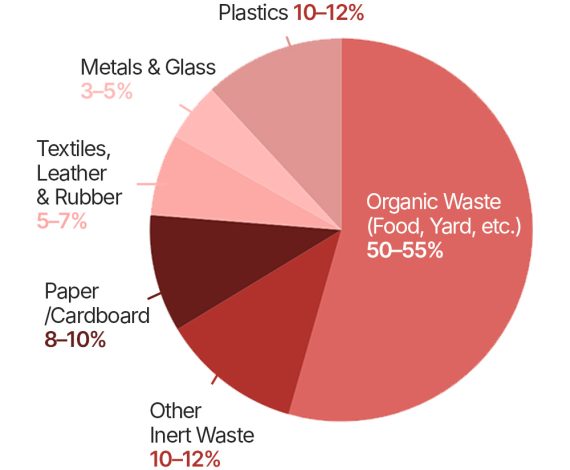
Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) is a high-calorific value fuel made from non-recyclable solid waste that would otherwise end up in landfills. It typically includes plastics, paper, packaging waste, textiles, and other combustible materials that cannot be composted or recycled economically.
These waste materials go through various processing stages—such as sorting, shredding (often using a plastic shredder machine), drying, and pelletizing—to create fuel suitable for use in cement kilns, power plants, and industrial boilers. RDF not only diverts waste from landfills but also replaces conventional fossil fuels, making it an eco-friendly energy alternative.
By integrating RDF into their operations, industries in India are embracing cleaner, more sustainable practices, aligning with the broader goals of municipal solid waste management in India.
RDF’s Role in Municipal Solid Waste Management in India
India’s growing cities are producing more waste than ever before. Traditional disposal methods like open dumping and landfilling are proving to be unsustainable, both environmentally and economically. This is where RDF plays a transformative role.
Incorporating RDF into municipal waste strategies helps reduce landfill burden, minimize methane emissions, and encourage the recovery of valuable energy from waste. Municipalities and industries are now recognizing RDF as a reliable fuel source that aligns with India’s climate goals and Swachh Bharat initiatives.
Moreover, RDF complements existing efforts like Material Recovery Facilities in India, where recyclable components are separated before the remaining material is processed into RDF. This integrated approach not only maximizes resource recovery but also promotes a circular economy.
How RDF is Produced – Step-by-Step Process
Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) isn’t just collected—it’s engineered through a systematic process to ensure quality and efficiency. Here’s how RDF is typically produced from municipal solid waste:
RDF Production Process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Waste Collection | Mixed municipal solid waste is collected from households, industries, and institutions. |
| 2. Pre-sorting | Recyclables and non-combustibles like glass, metals, and stones are separated. |
| 3. Shredding | A plastic shredder machine and other industrial shredders reduce the waste size for further processing. |
| 4. Drying | Moisture is reduced to improve the calorific value of the waste. |
| 5. Pelletizing | The dried material is compressed into RDF pellets, briquettes, or fluff for industrial use. |
Key Benefits of RDF in Waste Management
Refuse Derived Fuel isn’t just a by-product it’s a game-changer in how we handle waste in India. Here are some key benefits of RDF in solid waste management:
- Reduces Landfill Pressure: By diverting non-recyclable waste, RDF cuts down the volume of garbage sent to landfills.
- Lowers Carbon Emissions: RDF helps replace fossil fuels, significantly reducing CO₂ emissions in cement and power industries.
- Promotes Resource Recovery: RDF complements material recovery facilities in India by using leftover waste after recyclable materials are removed.
- Supports Government Initiatives: RDF aligns with India’s Swachh Bharat Mission and climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
- Cost-Efficient Fuel for Industry: For energy-intensive sectors, RDF offers a reliable and cost-effective alternative to coal and oil.
Arcler’s Role in RDF Processing Solutions
At Arcler, we specialize in designing and delivering end to end RDF and MSW processing plant solutions tailored to India’s evolving waste management needs. Our systems integrate advanced sorting, shredding, drying, and pelletizing technologies to ensure high-quality refuse derived fuel output.
Whether you’re a municipality, cement plant, or industrial unit seeking alternative fuel solutions, Arcler provides custom-built RDF systems designed for efficiency, compliance, and sustainability. Our solutions also work in sync with Material Recovery Facility in India, ensuring minimal waste, maximum recovery, and optimal energy value.
Conclusion: Turning Waste into Worth
India’s solid waste challenge demands smarter, greener solutions. Refuse Derived Fuel is not just an alternative fuel it’s a strategic tool in reducing landfill dependency, cutting emissions, and supporting the circular economy.
With innovations like RDF, and partners like Arcler, waste management in India is evolving from a burden to an opportunity. Whether you’re in government, manufacturing, or construction now is the time to invest in sustainable waste to fuel systems.
Ready to take the next step?
Explore our RDF processing solutions, or connect with us to transform your waste into valuable energy.





